Pollution Prevention

SII’s Environmental Policy emphasizes that "SII shall not only comply with laws, regulations, and other agreed-upon requirements, but also actively work to reduce environmental risks and prevent pollution." Additionally, "SII shall ensure the appropriate management of chemical substances used and those contained in our products."
Chemical Substances Control
Our Concept and Policy
Improper handling of chemical substances or equipment failure poses risks of environmental pollution and human injury. To mitigate these risks, it is essential to establish systems and procedures for the safe and effective control of chemical substances. Additionally, reducing the quantity of chemical substances used and replacing them with safer alternatives is crucial.
At each SII site where chemical substances are utilized, we implement activities focused on ensuring proper control and reduction. Specifically, we ensure safe handling methods and control by continuously implementing measures such as in-house education on chemical substance control, training for responding to emergencies like leaks, monitoring control through daily inspections and internal audits, and training qualified personnel. Furthermore, we promote reduction efforts by sharing information on alternative substances and methods for minimizing usage.
FY2023 Summary
In accordance with the annual plan for environmental activities, each business site conducted on-site checks through chemical substance management education, simulated emergency drills for potential chemical leaks, internal audits, and other measures to mitigate risks.
SII makes efforts to use the lowest amount of chemical substances. The FY2023 total emission of chemical substances subject to control in manufacturing process*1 was 15 tons, which was approximately 1.7 tons less than the total for FY2022. The amount of PRTR*2 substances handled was 46.2 tons, which was 2.9 tons less than the amount for FY2022. The increase is largely due to increased production.
SII makes efforts to use the lowest amount of chemical substances. The FY 2022 total emission of chemical substances subject to control in manufacturing process*1 was 16.3 tons, which was approximately 7.8 tons less than the total for FY 2021. The amount of PRTR*2 substances handled was 49.1 tons, which was 13.5 tons less than the amount for FY 2021. The increase is largely due to increased production.
*1 Of the chemical substances used in manufacturing processes, in addition to substances subject to the PRTR system, each domestic SII site aims to manage a reduction in the emission amounts of self-managed substances independently specified by SII (23 substances) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs)(100 substances).
*2 PRTR (Pollutant Release and Transfer Register): This system is designed to assess, gather, and disclose data on the volume of chemical materials handled, amounts released into the environment, and volumes transferred in waste materials to points outside the site locations. Companies collect data on the relevant substances and report them to the appropriate government agency once a year.

Breakdown of PRTR Substances (Amount handled and emitted)
FY 2023 PRTR Survey Results (SII sites in Japan only)
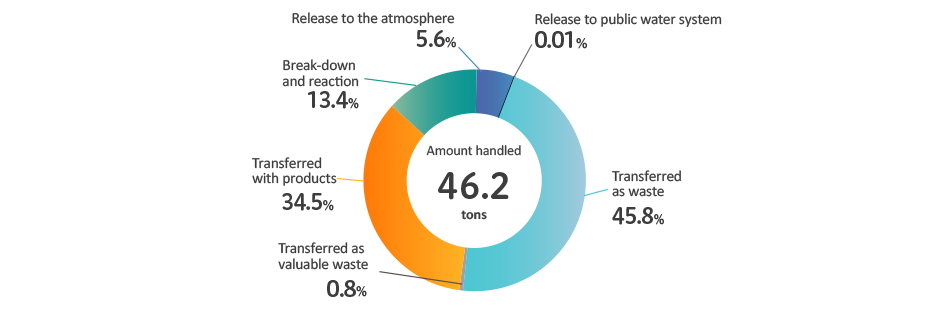
*Total may not become 100% due to rounding off.
| Chemical Substance | Amount Handled | Released | Transferred | Recycled | Consumed | Removed and Treated | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Released to the atmosphere |
2. Releases to public water systems |
3. Released to soil |
4. On-site landfill |
5. Transferred to sewage systems |
6. Transferred as waste |
7. Transferred as valuable waste |
8. Transferred as products |
9. Break-down and reaction |
||
| Ethylbenzene | 526 | 141 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 385 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Xylene | 2,704 | 169 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 638 | 0 | 0 | 1,897 |
| Cobalt and its compound | 9,699 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 348 | 9,340 | 0 |
| Toluene | 1,950 | 1,130 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 658 | 0 | 162 | 0 |
| Nickel compounds | 420 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 420 | 0 |
| Phenol | 1,418 | 213 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1,134 | 0 | 0 | 71 |
| Hydrogen fluoride and its water-soluble salts | 11,146 | 3 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10,580 | 0 | 0 | 557 |
| Manganese and its compounds | 7,083 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1,693 | 0 | 5,390 | 0 |
| Methylnaphthalene | 1,650 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1,642 |
| 239 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 239 | 0 | |
| trimethylbenzene | 2,748 | 32 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 680 | 0 | 0 | 2,036 |
| Lead compounds | 1,890 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1,511 | 0 | 379 | 0 |
| 4,726 | 876 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3,850 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 46,197 | 2,571 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 21,139 | 348 | 15,930 | 6,203 |
*There are some items that do not add up to the total due to fractional processing.
Measures against Ozone Depleting Substances
SII has completed the total elimination of specified fluorocarbons, which are ozone depleting substances, used in our manufacturing processes, however we still use fluorocarbons as refrigerant for chillers and air-conditioners. Our sites in Japan are in accordance with the Fluorocarbons Emissions Control Law and have been striving to prevent leaks during use in addition to disposal through conducting simple checks and periodic inspections.
Reduction of Environmental Risks
Our Concepts
In order to grasp and prevent environmental risks, it is important to understand what is considered a risk, and the effect on the environment when this risk occurs, risk prevention measures, and response methods when risks occur.
In order to grasp and prevent such environmental risks, SII educates through environmental education and internal audits.
Each site discovers and evaluates risks based on ISO 14001. The following are some of the risks that have been discovered.
- Risks of contamination of water quality, air, soil, and so on due to the discharge of toxic substances
- Risks of contamination following natural disasters
- Risks related to water
- Risks of deviation from various national environmental laws
In addition, SII is grasping climate change risks as its parent company Seiko Group Corporation deals with information disclosure through the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD).
Environmental Risk Countermeasures
To reduce risks, SII works out prevention measures and carries out daily inspections and emergency response training.
■Daily inspections
SII has wastewater treatment facilities, boilers, air conditioners, chemical tanks, and other environmentally related facilities and equipment. Periodic inspections and cleanings are carried out to prevent accidents and trouble.

■Training for emergencies
Each SII site considers environmental emergencies and has prepared countermeasures for them and procedure manuals for communication. While it periodically carries out emergency response training based on the procedure manuals to check their validity, SII puts into practice methods to prevent the spread of contamination.

Control of Chemical Substances Contained in Products
The tightened control of chemical substances contained in products has started from Europe and been expanded in all the countries of the world. SII has been working to prohibit or reduce the inclusion in our products of not only substances that have been banned by the laws and regulations, but also those for which there are concerns regarding their hazardous effects on human health and environment. All divisions engaged in products have established systems to promote activities to reduce their use and to prevent the inclusion in advance by performing periodic analysis and other measures.
Under the EU’s RoHS*1 directive, four phthalate esters were added as restricted substances in July 2019. SII has carried out replacement of such items with substitutes and has completed these replacements for the products intended for the EU market that are subject to the directive in May 2019, and we are also progressively carrying out such replacements for all of our products.
In addition, in regard to an application for an extension of exemptions related to SII with a deadline of July 2021, a final report was released in January 2022 by a consultant commissioned by the European Commission. In the final report, the conditions have become stricter, such as shortening the period of extension applied for, according to the exemption items, and applying the extension of exemptions only to specific products. The report will be discussed by the EU Commission and published in the Official Journal, but it is possible that the exemptions will become stricter than the current ones. *2
With the understanding that the exemption under RoHS Directive is not permanent, SII is developing new products using materials that do not contain lead, and for existing products, we are continually conducting tests to explore the possibility of substituting certain materials, and has achieved substitutions for products with favorable results.
We continue to monitor the trend of exemption and work on developing our technology for finding alternative methods, taking into account the environmental impact and the economic perspective.
The REACH regulation*3 requires that information on substances of very high concern*4 (SVHCs) contained in products be communicated to customers and other parties, as well as notification to the EU authorities based on the quantity shipped to the EU. New substances are added to SVHC every year and there are 240 substances as of June 2024.
SII continues to check their inclusion in our products, and based on the results, we will fulfill our obligations while reducing the use of SVHC and finding the substitutes.
As legislation to regulate PFAS*5 is being introduced in Europe and the United States, where notification of products containing PFAS is now required, it has become essential to determine whether these substances are present in products and in what quantities. Given the diverse types and applications of PFAS, we will continue to monitor legislative trends and conduct surveys as necessary.
*1 RoHS Directive restricts the use of six hazardous materials found in electrical and electronic products: Lead (Pb), Cadmium (Cd), Mercury (Hg), Hexavalent chromium (Cr6+), Polybrominated biphenyls (PBB), and Polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE). DEHP, DBP, BBP, and DIBP have been added to RoHS Directive since July 22, 2019.
*2 Extension approval: Next deadline date and conditions will be set. Extension denial: Exemption will expire after a grace period of 12-18 months. If no decision is reached by the due date, the deadline will be extended until a decision is made.
*3 REACH Regulation: The regulation describe about registration, evaluation, authorization, and restriction of chemicals in the EU.
*4 SVHC (Substances of Very High Concern): Substances of very high concern that are candidates to be listed in Annex XIV of REACH. The substances are included in the Candidates List.
*5 PFAS: A general term for perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl compounds, with over 12,000 types identified. Among these, PFOS, PFOA, and PFHxS have been designated for elimination under the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs). In Japan, their manufacture and use in products are prohibited under the Law Concerning the Examination and Regulation of Manufacture, etc. of Chemical Substances (Chemical Substances Control Law).



